A plug valve is a type of valve that uses a rotating plug to control flow and shut-off. Its core advantages are fast opening and closing speed, low flow resistance due to a straight-through flow path, and a simple and wear-resistant structure. Its disadvantages include sealing performance being significantly affected by plug wear, and higher maintenance costs for sealing under high pressure and high temperature conditions. It is mainly suitable for large diameter, low to medium pressure, and clean media applications, but can also be used for conveying media containing particles or viscous fluids. It is a commonly used valve in the petroleum, chemical, metallurgical, and water supply and drainage industries.
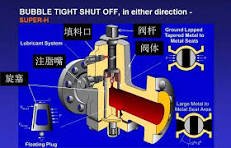
Its core application scenarios and specific uses are summarized by industry below, along with applicable/inapplicable conditions for easy selection reference:
I. General Core Uses (All Industries)
Fast Opening and Closing: The plug rotates 90° to achieve full open/full close, suitable for pipelines requiring rapid operation, such as emergency shut-off, pipeline switching, and media diversion/combination (three-way/four-way plug valves).
Low Resistance Conveying: The straight-through flow path has no throttling steps, and the media flow resistance is far less than that of gate valves and globe valves, suitable for pipelines requiring high flow rates and low pressure loss.
Conveying Media Containing Particles/Viscous Fluids: The gap between the plug and the valve seat is relatively large, making it less susceptible to jamming by solid particles. It can be used to transport mud, slurry, crude oil, heavy oil, sewage, and other media containing impurities or viscous fluids (wear-resistant materials such as cast iron and stainless steel should be selected).
II. Specific Application Scenarios by Industry
1. Oil and Gas Industry (The most important application field)
Oilfield Exploration: Wellhead manifolds, oil and gas gathering and transportation pipelines, used for the shut-off and diversion of oil, gas, and water mixed media, adapting to the rapid operation needs of oilfield sites;
Oil and Gas Storage and Transportation: Oil/gas pipelines, storage tank inlets and outlets, large-diameter plug valves are used for on/off control of large-flow media;
Refining and Petrochemical Processes: Low-pressure process pipelines (such as fuel oil and lubricating oil transportation), avoiding the wear and tear on the plug seal caused by high pressure and high temperature. 2. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
Basic Chemicals: Low-pressure pipelines for dilute solutions of acids, bases, salts, solvents, and inert gases (nitrogen, argon). The corrosion resistance of plug valves can be achieved through fluoropolymer or rubber lining;
Coal Chemical/Coking: Pipeline shut-off for media containing impurities such as coal gas, tar, and ammonia water, suitable for viscous media containing small amounts of particles;
Pharmaceutical Intermediates: Low-pressure pipelines for clean media (such as pure water, alcohol), using food-grade stainless steel plug valves to meet hygiene requirements.
3. Metallurgy and Mining Industries
Metallurgical Smelting: Pipelines for blast furnace gas, cooling water, and dust removal water. Large-diameter plug valves are suitable for high-flow industrial water/coal gas transportation in metallurgical plants;
Mining: Pipelines for ore pulp, mud, and tailings water. Wear-resistant plug valves prevent clogging by particulate media and are suitable for harsh mining conditions;
Non-ferrous Metal Processing: Low-pressure pipelines for electrolytes and dilute acid solutions. Fluoropolymer-lined plug valves provide corrosion resistance.
4. Water Supply and Drainage and Municipal Engineering
Urban Water Supply/Drainage: Large-diameter pipelines in municipal networks and sewage treatment plants, used for quick shut-off during water source switching and pipeline maintenance;
Fire Protection Systems: Emergency shut-off valves for fire water pipelines, suitable for rapid opening and closing during fires (fire-specific plug valves should be selected);
Building Water Supply and Drainage: Small-diameter pipelines for floor water supply branches, bathrooms/balconies. Plug valves have a compact structure and are easy to install and maintain.
5. Food and Beverage and Paper Industries
Food and Beverage: Transportation of viscous media such as fruit juice, syrup, and edible oil. Food-grade plug valves have no dead ends and are easy to clean, meeting hygiene standards;
Paper Industry: Pipelines for pulp, white water, and black liquor. Wear-resistant plug valves are suitable for transporting fibers and impurities in pulp, preventing clogging. 6. Marine and Offshore Engineering
Ship Piping: On/off control of cooling seawater, fuel oil, and ballast water; plug valves are resistant to seawater corrosion (using brass and stainless steel materials) and are suitable for the limited space and rapid operation requirements of ships;
Offshore Platforms: Low-pressure oil and gas gathering and transportation, fire water pipelines, meeting the corrosion resistance requirements of the marine environment.
III. Applicable/Inapplicable Working Conditions of Plug Valves
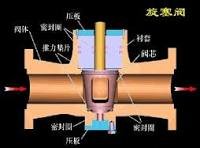
✅ Applicable Working Conditions
Pressure: Low to medium pressure (usually PN≤40, high pressure requires special hard-sealed plug valves, which are more expensive);
Temperature: Ambient to medium temperature (-20℃~350℃, seals are prone to aging at high temperatures, leading to reduced sealing performance);
Medium: Clean media, media containing a small amount of particles, viscous media, inert gases, non-corrosive/weakly corrosive liquids;
Nominal Diameter: Small (DN15) to large (DN1000+) diameters are all possible, with the advantages being more pronounced for larger diameters;
Operation: Manual, pneumatic, and electric operation are all possible, with pneumatic/electric operation suitable for rapid opening and closing of automated pipelines.
❌ Inapplicable Working Conditions
Harsh high-pressure and high-temperature conditions (such as power plant main steam pipelines, high-pressure chemical reactor inlets and outlets), where seals are prone to failure;
Vacuum pipelines and high-purity media pipelines (such as electronic-grade ultrapure water, high-purity gases) that require extremely high sealing accuracy;
High-pressure pipelines for highly corrosive media (such as concentrated nitric acid, concentrated hydrochloric acid) (fluorine-lined plug valves are only suitable for low-pressure and highly corrosive conditions);
Pipelines requiring precise throttling control (the valve core is prone to wear during throttling, and the adjustment accuracy is far lower than that of control valves and needle valves). IV. Extended Applications of Special Types of Plug Valves
Three-way/Four-way Plug Valves: Used for switching, diverting, and combining pipeline media, such as the separation of oil, gas, and water in oil pipelines, and the mixing of two media in chemical pipelines;
Fluorine-lined Plug Valves: Suitable for low-pressure corrosive media, such as the transportation of dilute sulfuric acid, hydrofluoric acid, and caustic soda solutions in the chemical industry;
Oil-sealed Plug Valves: Enhanced sealing performance through oil seals, suitable for medium-pressure oil and gas pipelines, improving sealing reliability;
Track Plug Valves: Hard-sealed structure, suitable for medium-to-high pressure and medium-to-high temperature conditions, compensating for the high-pressure limitations of ordinary plug valves, and used in high-pressure manifolds in oil fields and medium-pressure process pipelines in the chemical industry.




